Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- CASE Ingredients Functions
- CAS No.
- 919-30-2
- Molecular formula
- C₉H₂₃NO₃Si
- EC No.
- 213-048-4
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Chemical Structure
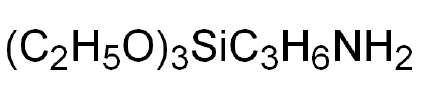
Features & Benefits
- CASE Ingredients Features
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Compatible Polymers & Resins
- Coating Type
- Applications
- Building & Construction Adhesives
- Interior Paints
- Sealants
- Flooring Installation
- Waterproofing Membranes
- Application Details
General processing information:
- GENIOSIL GF 93 is highly miscible with standard organic solvents, such as ethers and hydrocarbons. Mixing with ketones results in imine formation, while mixing with alcohols other than ethanol leads to an autocatalytic exchange of alkoxy groups until the system reaches thermodynamic equilibrium. GENIOSIL® GF 93 shows typical amine behavior when exposed to acids, epoxides or isocyanates.
- GENIOSIL® GF 93 is highly soluble in neutral water and undergoes hydrolysis. Caution: due to the enthalpy of solution, mixing GENIOSIL® GF 93 with water is exothermic. A solution of GENIOSIL® GF 93 in water has a pH of 10 - 11 and remains stable for several weeks. Due to the highly reactive nature of GENIOSIL® GF 93, contact with moisture must be avoided during processing to prevent undesired hydrolysis.
GENIOSIL® GF 93 as a surface modifier:
- Fillers are treated either with pure GENIOSIL® GF 93 or a solution thereof. It may be necessary to pretreat the substrate with water.
- The modified filler is preferably bonded to the organic material, e.g. an epoxy resin, by mixing it with a standard curing agent.
- In an alternative procedure referred to as "blending", GENIOSIL® GF 93 is added directly to the polymer - either before the organic materials is compounded with the filler or at the same time.
- A prerequisite for the blending process is that GENIOSIL® GF 93 and the polymer are compatible and that the resin and GENIOSIL® GF 93 do not react prematurely.
GENIOSIL® GF 93 as an adhesion promoter in formulations:
In silane crosslinking formulations (e.g. silane-terminated polyethers or polyurethanes and polysiloxanes), GENIOSIL® GF 93 may be added to the formulation as an adhesion promoter. Processing is effected by means of standard mixing methods. Usually, about 1 - 2 wt % silane is added to the formulation.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Soluble in
- Water
- Miscible in
- Hydrocarbons, Ethers
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Amine Number approx. 4.5 mmol/g WSTM 1297A Molecular Weight 221.4 g/mol - Boiling Point (at 1013 hPa) 217 °C - pH 10 -11 - - Density (at 25°C) 0.94 g/cm³ DIN 51757 Dynamic Viscosity (at 25°C) approx. 1.6 mPa·s DIN 51562 Flash Point 93 °C ISO 2719 Purity min. 97 % - Refractive Index (at 25°C) 1.42 - - - Properties
- In addition to its application as an adhesion promoter in formulations and primers, GENIOSIL® GF 93 functions as a surface modifier in fillers and pigments, where it improves the dispersibility of the filler and the mechanical properties - such as flexural strength, tensile strength and modulus - of the composites. The silane also reduces the filler's sedimentation tendency in the uncured polymer. GENIOSIL® GF 93 also greatly increases water (vapor) and corrosion resistance.
- Due to the nature of the amino group, this substance reacts as a strong base. The silane hydrolyzes autocatalytically in the presence of moisture (Ethanol is released) to form silanols, which can subsequently react with themselves to produce siloxanes or can bind to inorganic substrates. As a typical amine, GENIOSIL® GF 93 can also interact with numerous organic polymers and thus function as a molecular bridge between organic and inorganic substrates.
Packaging & Availability
- Country Availability
- Regional Availability