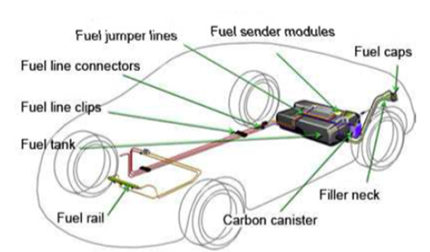
In their continuous search and efforts over the last decades to reduce weight in cars, the automotive industry has been replacing more and more metals by thermoplastic based solutions. The fuel management area is not exempt from that. Fuel pumps, filler necks, filters, inlet check valve housings, line clips, delivery modules, filter housings etc can be designed out of LNP STATKON® compounds that meet the need of this important segment.
Fuel Delivery and Sparking
When operating with standard (non electrically conductive) plastics in an environment of fuel, petrol and other automotive fluids, there are always 2 main concerns that need to be addressed. 1) Due to electrostatic charging effects, the fuel delivery will get impeded and lead to an inconsistent material flow and 2) Sparking and electrostatic discharging effects represent an immediate fire risk.
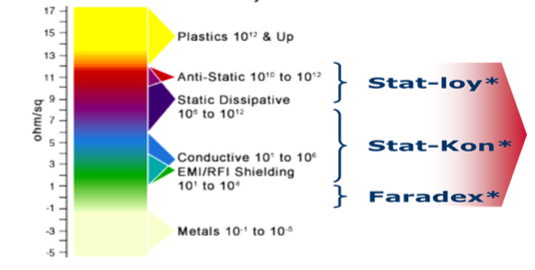
Electrically Conductive Compounds
The addition of a conductive filler to a thermoplastic material can increase the electrical conductivity and herewith reduces the risks for electrostatic charging and discharging. Traditional fillers like carbon powder and fibers are effective, and more novel and advanced technologies can provide additional features . Since resistance to fuel and other automotive liquids is a prime CTQ, compounds are always based on semi-crystalline resins
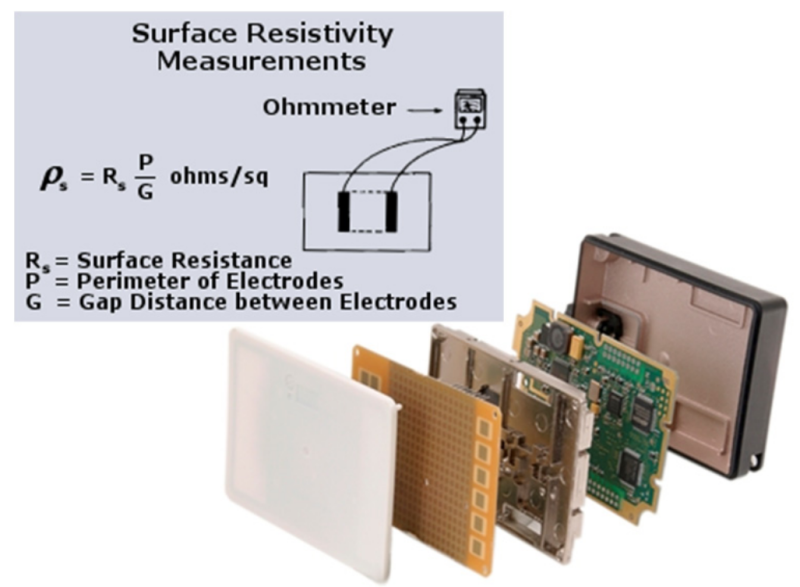
Measuring Performance
The before mentioned risks associated with electrostatic charge build up need to be mitigated. The requirements for components that come in contact with liquid fuel are driven by the OEM’s and are specified in the SAE J1645 standard. According this standard the surface resistivity before and after fuel soak should not exceed 10E6 Ω/sq. The retention of properties after extended fuel exposure applies also to the other functional requirements for mechanical and thermal performance
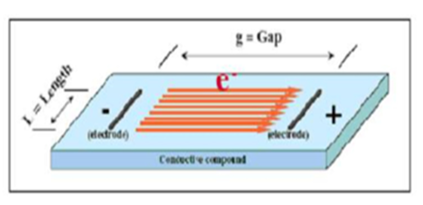
Sr=Rs(L/G)
L = Length of Electrodes
G = Gap Distance Between Electrodes