Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Ingredient Name
- Animal Feed & Nutrition Functions
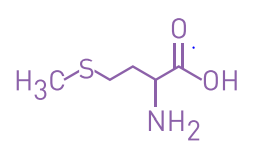
- Molecular formula
- C5H11NO2S
- Molecular Weight
- 149.21
- Ingredients
- L-Methionine
- Technologies
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Animal Feed & Nutrition Features
- Main Benefits Of L-methionine
Excellent bio availability
- Through a series of experimental trials in several internationally-recognized research institutions, L-Methionine has consistently shown a higher relative RBA than DL-Met on FCR, ADG and final body weight.
Fermentation based
- CJ L-Methionine is produced with an innovative fermentation processes using raw sugar, thus combining sustainability and efficiency in animal nutrition
L-Isomeric form of Methionine- Naturally occurring amino acids are all in the L-form (Wikipedia, chirality)
- According to Section 172.320 of FDA's code of federal regulations title 21, only
L-Met is suitable as a food additive for infants.
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Why Young Animals Prefer L-Methionine (BLL)?
In order for D-amino acids to be oxidized in vivo by D-AAO and D-Asp, they first must be absorbed from the intestine, enter into the bloodstream and be transported
to the liver and kidneys. Research showed that the expression of this enzyme is very low for young animals (D'Aniello et al., 1993).
Therefore, L-Met is the only L-ME biologically functional form of Met readily utilized by the intestinal cells of young animals. The growth and development of the gastrointestinal tract requires a variety of functions of AA a metabolism, including protein synthesis, cell signaling, antioxidative function, and immune function (Shoveller et al., 2003).Metabolism of essential AA by the mucosal cells is quantitatively greater than AA incorporation into mucosal protein (Stoll et al., 1998). Methionine is also a precursor for Cys, which plays a key role in maintaining protein function and redox status. In addition, Met serves as an indirect precursor of GSH (through Cys), taurine, Methionine and inorganic sulfur, which are also major cellular antioxidants (Brosnan and Brosnan, 2006).
Therefore, the functional role of Met in the gastrointestinal tract, especially its antioxidative effect, may be the key effects on the health of the gastrointestinal tract health of a rapid growing animal and consequently impact its growth potential (Shen et al., 2014).- The Theory of BLL
- D-form amino acids must be oxidized (racemization) to mobilize in the body (i.e. anabolism and catabolism).
- This oxidization process requires enzyme reaction. Iracemase; e.g. D-AAO, D-Aspo). Its occurrence (activation) is increased by the age in animal.
Properties
- Typical Properties
| Value | Units | Test Method / Conditions | |
| L-methionine | min. 99 | % | - |
| Moisture Content | max. 0.5 | % | - |
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type

