Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Name
- Ingredient Name
- Animal Feed & Nutrition Functions
- CAS No.
- 156-54-7
- Ingredients
- Sodium Butyrate
- EC No.
- 205-857-6
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Contents
Active Substance
- Sodium butyrate (stabilizing additive E470)
- Aromatic substances
Features & Benefits
- Animal Feed & Nutrition Features
- Benefits
- Increased surface area
- Destruction of harmful bacteria
- Improved nutrient absorption capacity
- Stronger and higher villi
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Animal Species
- Poultry Applications
Drake, turkey-hen, broiler & layer, By water as follows:
- Add 1.1 – 1.6lbs to 5 gallons of water to make a stock solution.
- Meter out at 1oz. per gallon of drinking water.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Appearance
- White powder
- Chemical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Density 0. 70 - 0.80 g/cm³ - Moisture Content 13 % - Particle Size 50 - 100 μm - - Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions pH 9.9 - - - Analytical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Crude Ash 57 % - Phosphorous Content 2.3 % - Sodium Content 24 % -
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
Technical Details & Test Data
- Introduction
- Enteric disease such as necrotic enteritis (NE), caused by Clostridium perfringens, has been commonly diagnosed in the poultry industry, causing severe economic losses such as decreased productivity and increased mortality
- With increasing attention being given to raising broilers without the use of antibiotics, efforts have been made to evaluate various alternatives for the industry
- Butyric acid has been identified as a potential feeding strategy for managing NE in broilers raised without antibiotics
- This study was conducted to compare the effect of butyric acid (SmartFeedsUSA) when added in either the feed or the water on growth performance and the alleviation of NE
- We hypothesized that butyric acid lessens the impacts of NE and that the effects differ based on method of application
- Materials and Methods
- 160 Cobb-Cobb male one-day-old chicks, allocated into treatment pens (8 birds/pen)
- Completely randomized design, 4 treatments with 7 replicates of both non-challenged control (NCC) and challenged control (CC), 3 replicates of the water treatment (WT) and feed treatment (FT)
- Oral gavaged with ~5000 Eimeria maxima oocysts on day 14
- On day 19, 20 and 21, the challenged birds received 108 cfu/ml Clostridium perfringens by oral gavage
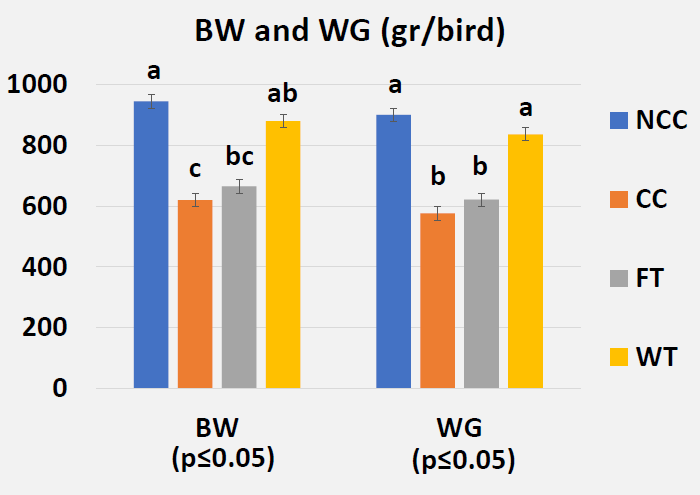
- Body weight and feed intake were recorded on day 14, 21 and 28, and mortality was recorded daily
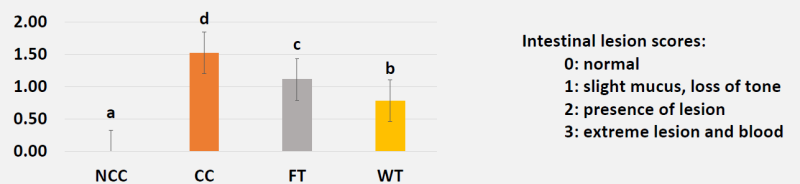
- Intestinal lesions were scored (3 birds/pen) on day 21
- Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA via SPSS, with significant differences (P ≤ 0.05) separated by Duncan’s Multiple Range Tests
- Effects of Butyric Acid on Growth Performance on Day 14 (Pre-Challenge)
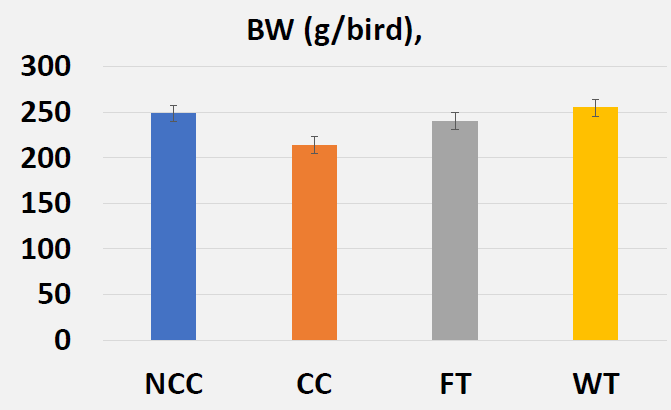
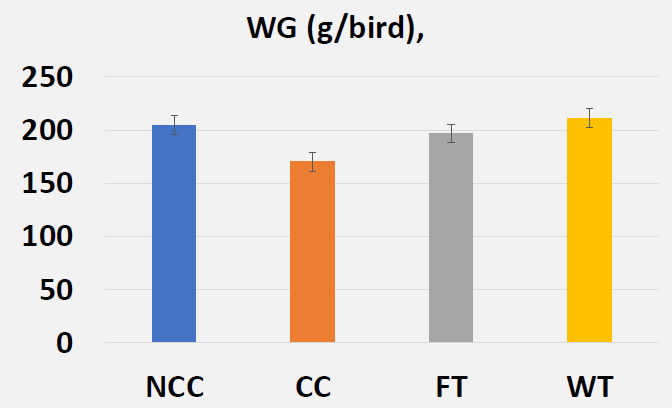
- Effects of Butyric Acid on Growth Performance on Day 21 (Post-Challenge)
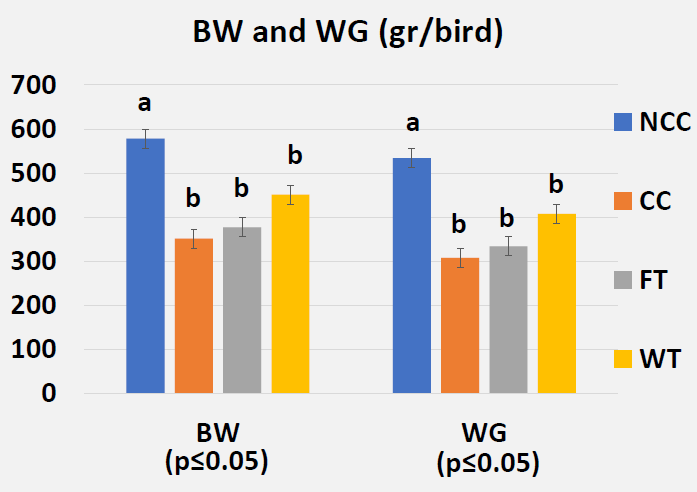
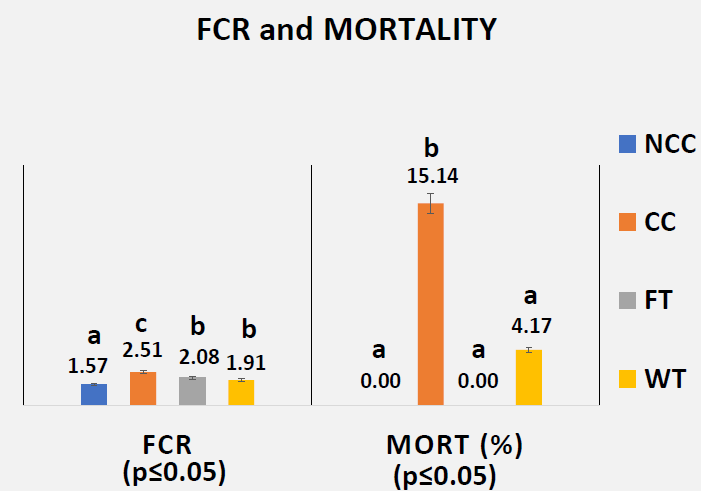
- Necrotic Enteritis Lesion Scores on Day 21
- Effects of Butyric Acid on Growth Performance on Day 28 (Post-Challenge)
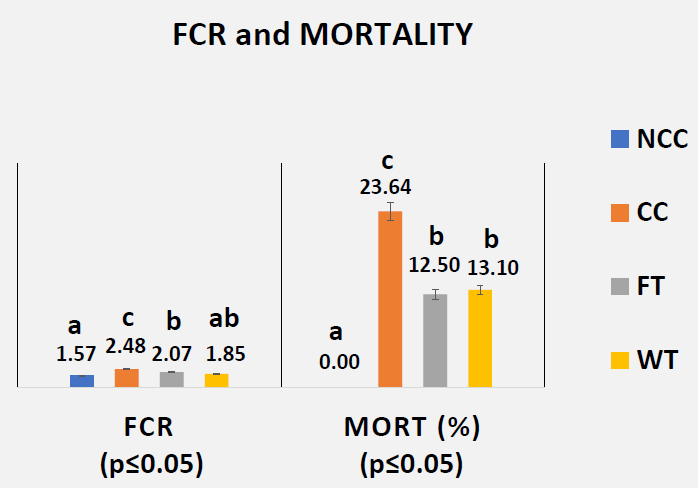
- Conclusion
We were able to confirm both hypotheses :
- Butyric acid offered benefits to growth, gut health, and livability in NE-challenged broilers over the control
- Further, a drinking water application showed a greater effect than that seen with a feed application
Safety & Health
- First Aid Measures
- Eyes : Flush with water for 15 minutes, keeping eyelids open. Seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Skin : Flush with water, then wash with soap and water. Remove contaminated clothing.
- Inhalation : Leave the contaminated place and move to fresh air. Seek medical attention if necessary.
- Ingestion : Drink 2 to 3 glasses of water. Seek medical advice if it feel faint. In case of serious and persistent symptoms, consult a doctor.
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 24 months
- Storage and Shelf Life
- Store in dry facility until ready to mix.
- Product active 24 months from the date of manufacture.
- Heat stable at 250 ° C