Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Reinforcement Form
- Composite Materials Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Materials Features
- Material Benefits of Sigrafil Chopped Carbon Fibers
- Excellent mechanical properties
- Low density
- Low thermal expansion
- Good electrical conductivity
- Corrosion resistant
- Excellent feedability
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Composites Processing Methods
- Typical Customer Products and Processes
- Thermoplastic compounds for injection molding
- Coating systems
- Anti-static and fire protection
- Adhesives
- Speciality papers
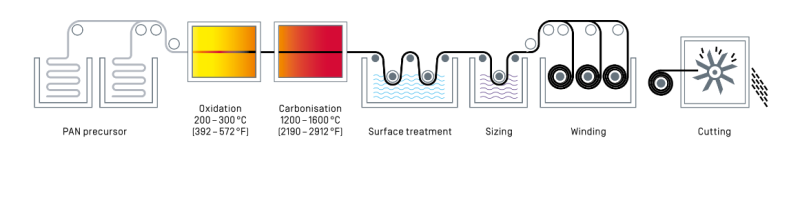
- Manufacturing process of Sigrafil® C C6-4.0240-G100
- The Best Carbon Fiber for Each Application
Our carbon fibers are available coated with various sizings and in different staple lengths to ensure consistently optimum fiber dispersion whatever the application, e.g. for thermoplas- tics, thermosets or aqueous processes.
For the production of compounds, we supply carbon fibers with special sizings. These are perfectly matched to the processing temperatures and bonding characteristics of the different thermoplastics. With our different SIGRAFIL materials, you can choose the specific carbon fiber property that you need.
Whether you are using carbon fibers as a reinforcing material or a filler, their properties can be transferred to your compounds and composites and ultimately to the end products. This opens up many different possibilities for you.
Properties
- Physical Form
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Compatible With Water-based systems - - Density 1.8 g/cm³ - Elongation at Break 1.7 % - Fiber Length Chopped 6.0 mm - Single Filament Resistivity 15.0 μΩm - Sizing Type Glycerin - - Sizings Mass Content 4.0 % - Tensile Modulus 240.0 Gpa - Tensile Strength 4.0 Gpa - Filament Diameter 7 μm
Technical Details & Test Data
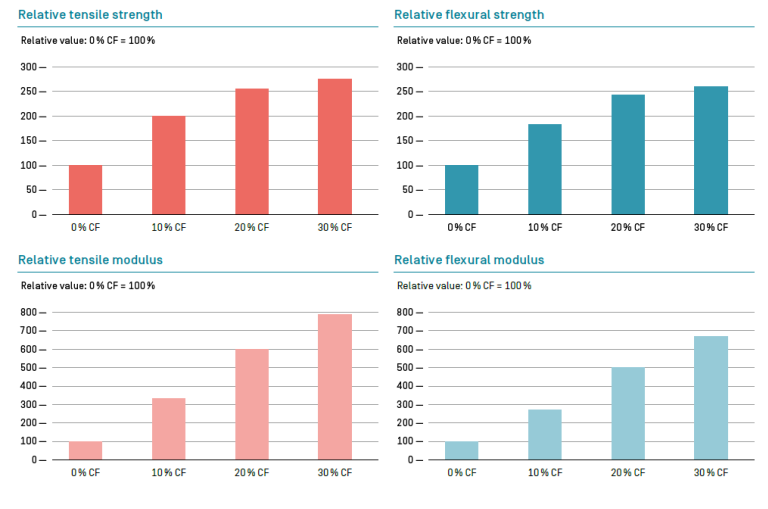
- Relative Properties of Chopped Carbon Fibers in Poly Carbonate
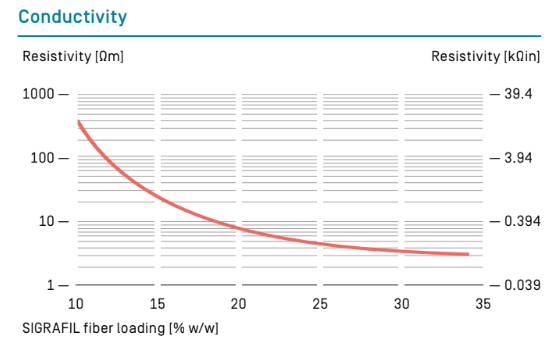
In the production of compounds, chopped carbon fibers are traditionally used as a filler material. By varying fiber staple length and loading. it is possible to control how strongly a particular carbon fiber property is expressed in the compound. With higher fiber loading. there is a corresponding decrease in electrical resistivity and hence an increase in conductivity. Higher conductivity also results in better electromagnetic shielding. Similar behavior can be seen in the mechanical properties of our carbon fibers. With higher filler loading in the compound, stiffness and strength are increased, although the rise in stiffness is far greater.