Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- CAS No.
- 2375046-39-0
- Technologies
- Product Families
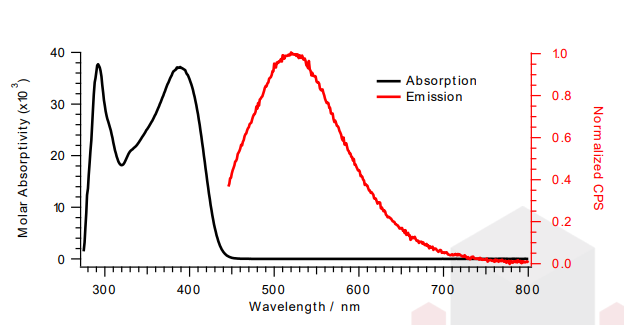
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Features
- Strong reductant
- Energy transfer sensitizer
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Applicable Processes
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Application Notes
- C-N, C-O, C-S, and C-C crosscouplings
- Reduction of alkyl halides for vinyl or aromatic addition/ substitution (e.g. trifluoromethylation)
- Atom transfer radical polymerization
Properties
- Physical Form
- Physical Properties
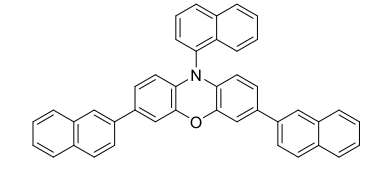
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Purity min. 97 % - Maximum Soluibility Water (25°C) TBD - - Maximum Soluibility DMSO (25°C) TBD - - Maximum Soluibility MeOH (25°C) TBD - - Maximum Soluibility DMF (25°C) TBD - - Maximum Soluibility MeCN (25°C) TBD - - Maximum Soluibility DCM (25°C) TBD - - Maximum Soluibility Toluene (25°C) TBD - - Scientific Name 10-(naphthalen-1-yl)-3,7-di(naphthalen-2-yl)-10Hphenoxazine - - Formula C₄₂H₂₇NO - - Molecular Weight 561.68 - - Appearence Yellow Powder or Crystals - - - Typical Properties
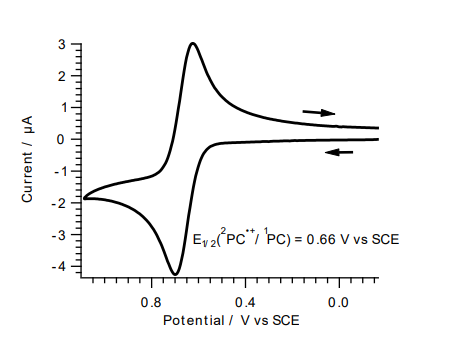
Value Units Test Method / Conditions E⁰(²PC⁺/¹PC) -1.72 V - E₁/₂(²PC⁺/¹PC) 0.66 V - Epsilon Max(abs) 37200 M⁻¹cm⁻¹ - Lambda Max,(abs) 389 nm - Lambda Max,em 522 nm -
Technical Details & Test Data
- Technical Details
Phenoxazine PCs are strong excited state reductants capable of reducing alkyl and aryl halides via an electron transfer mechanism. The alkyl radicals formed can partake in substitution or addition reactions on unsaturated vinyl or aromatic groups e.g., atom transfer radical polymerization, atom transfer radical addition and trifluoromethylation. This class of PCs can also activate Ni co-catalyst for C-N, C-S, C-O and C-C aryl cross-coupling reactions. In the case of C-N cross-coupling, spectroscopic evidence suggests that phenoxazine PC activates a Ni-amine co-catalyst via an energy transfer mechanism. Additionally, these PCs have been demonstrated in solar fuel generation converting CO₂ to methane, thus closing the carbon cycle.
- Current Vs Potential
- Molar Absorptivity Vs Wavelength