Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Fillers Included
- Polymer Name
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Materials Features
- Product Features
- Esd additives for static dissipation
- Mica-filled PTFE for low deformation under load resistance
- Low CLTE for improved stability compared to other filled PTFEs
- Thermal performance to 500°F (260°C)
- Thermally insulative
- Very low coefficient of friction
- Broad chemical resistance
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Plastics & Elastomers End Uses
Properties
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Technical Details & Test Data
- Engineering Notes
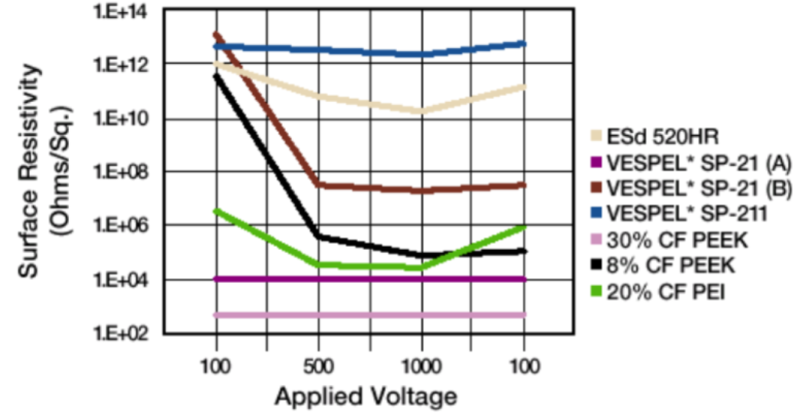
It is important to know how applied voltage affects the resistance of a material. Some materials exhibit high resistance at low voltages, but when subjected to harsher conditions, they can fall. This is due to dielectric breakdown and is irreversible. This chart illustrates the effect of sequential applications of 100 through 1,000 volts, then a return to 100 volts to determine the hysteresis. Since static electricity can be several thousand volts, consistent performance across the voltage range must be considered.
Some materials are very inconsistent and vary on the "grain" of machining. One pair of lines illustrate the typical variation from side to side (A to B) of the same sample. This example demonstrates the need for consistent behavior in service.