Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- CASE Ingredients Functions
- Fluids & Lubricants Functions
- Industrial Additives Functions
- CAS No.
- 143-23-7
- EC No.
- 205-593-1
- Technologies
- Product Families
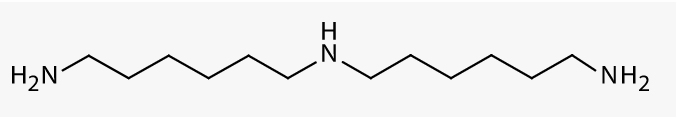
- Molecular Structure
Features & Benefits
- CASE Ingredients Features
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Compatible Polymers & Resins
- Compatible Substrates & Surfaces
- Industrial Additives End Use
- Epoxy Curatives
Epoxy resins cured with Dytek® amines have excellent properties for use in coatings, civil engineering, adhesives, marine, and composite applications.
- Applications
- Asphalt anti-stripping agents
- Cationic emulsifying agents
- Cationic collectors for ore flotation
- Chelating agent
- Corrosion and scale inhibitors
- Curing agents for urethanes
- Curing agents for epoxy resins
- Flocculating agents
- Wet strength paper resins
- Polyurethane chain extender or catalyst
- Polyamide resins for Adhesives, Films, Inks, Plastics, Wet strength paper resins
- Epoxy curing agent
- Liquid Anti-Strip Agents
Moisture causes many common pavement distresses such as potholes, raveling, and rutting. Moisture related damage in asphalt concrete occurs when water removes, or “strips”, the asphalt binder from aggregate surfaces. Scientists and engineers developed anti-strip technologies in response to this serious and expensive problem that greatly decreases pavement ride quality and the expected life span of our roadways.
Liquid Anti-strip agents are liquid chemical additives added to asphalt mix to increase the occurrence and strength of asphalt to aggregate adhesion, which mitigates stripping and the deterioration of the asphalt. Common liquid anti-strip additives based on amine chemistry include:
- Ethylene amines
- Polyamines
- Fatty (tallow) amines
- Amidoamines
Dytek® BHMT is among the best amine liquid anti-strip additives in prolonging the service life of asphalt
Properties
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions 6-Aminocaproamide Content 1–3 wt% - Amine Value 474-736 mgKOH/g - Bis(hexamethylene)triamine Content 25–85 wt% - Boiling Point (100 mmHg with decomposition) 249 (480) °C (°F) - C10 Amines Content 1-4 wt% Caprolactam Content 3–5 wt% - Flash Point 121 (250) °C (°F) Open Cup Hexamethylenediamine Content 1–3 wt% - Melting Point (Pure component) 32–34 (90-93) °C (°F) - Oligomeric Amines Content 6–70 wt% - Specific Gravity 0.93–0.97 - - Vapor Pressure (at 180°C (356°F), Pure component) 7 mmHg -
Technical Details & Test Data
- Dytek® BHMT - Prolonging the Service Life of Asphalt
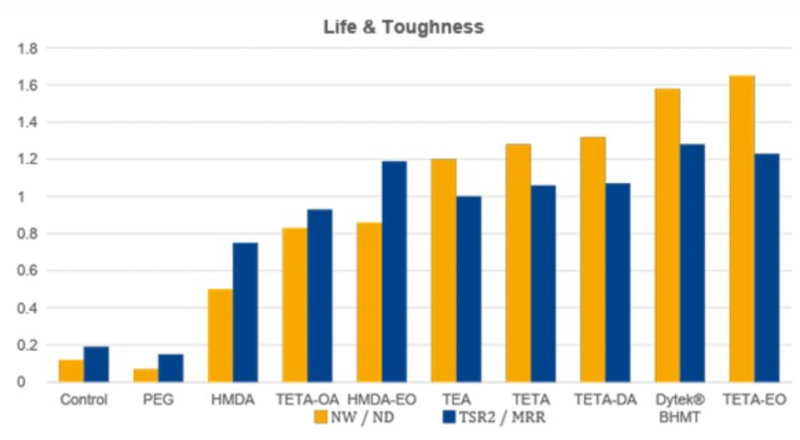
Additives Description :Control No LAS Additive PEG Polyethylene Glycol HMD Hexamtheylenediamine TETA-OA TETA - Oleyl Amide HMD-EO HMD - Ethylene Oxide adduct TEA Triethanolamine TETA Triethylenetetramine TETA-DA TETA - Dioleyl Amide Dytek® BHMT Bis(hexymethylene)triamine TETA-EO TETA - Ethylene Oxide adduct Measurements used to quantitatively describe the moisture damage on changes to adhesion and cohesion in an asphalt mix
TSR Tensile Strength Ratio Decrease in TSR => loss of cohesion │ softening by water MR Resilient modulus High MR => increase in stiffness; may lead to poor fatigue life Nw/ND Ratio of wet life to dry life a measure of the effectiveness of chemical in improving the service life of asphalt │ higher the value, better the performance (TSR)2/MRR Toughness ratio Alternative to NW/ND │ larger value preferred
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Information
Tank truck Net Weight : 45,000/20,400 (lbs/kg) Drums Net Weight : 400/181 (lbs/kg)