Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Animal Feed & Nutrition Functions
- Ingredients
- Barley, Oats, Fructo-Oligosaccharide, Saccharomyces Cerevisiae, Beta-Glucans, Mannan-Oligosaccharide, Xylooligosaccharides, White Wheat, Flaxseed, Brown, Arabinoxylo Oligosaccharide
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Animal Feed & Nutrition Features
- Key Attributes
- Made from Wheat, Oats, Barley and Flax
- 4 Prebiotic Fibers
- Omega 3 and Amino Acids
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Animal Species
- Product Applications
- Cattle
- Poultry
- Sheep
- Swine
- Horses
Properties
- Physical Form
- Physical Form
- Powder
- Physico-Chemical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Particle Size 160.0 μ - pH 4.3 - 5.2 - - Moisture Content 7 - 12 % - Ash Content 12.0 % - Bulk Density. 34 - 38 lb/ft3 - - Nutritional Information
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Crude Protein min. 28.00 % - Crude Fat min. 7.00 % - Crude Fat (as Omega 3) min. 2.00 % - Crude Fiber max. 8.50 % - ADF Fiber max. 9.50 % - NDF Fiber min. 25.00 % - Calcium Content 0.10 - 0.15 % - Phosphorus Content min. 3.00 % - Magnesium Content min. 0.40 % - Sodium Content 0.80 - 1.10 % - Potassium Content min. 1.00 % - Sulfur Content min. 0.30 % - Selenium Content min. 0.9 ppm - Cobalt Content min. 1.0 ppm - Iodine Content min. 0.6 ppm - Iron Content min. 100 ppm - Copper Content min. 15 ppm - Manganese Content min. 100 ppm - Zinc Content min. 100 ppm - Alanine 1.19 % - Arginine 1.85 % - Aspartic acid 1.91 % - Cystine 0.6 % - Glutamic acid 7.66 % - Glycine 1.44 % - Histidine 0.72 % - Isoleucine 1.16 % - Leucine 1.9 % - Lysine 0.88 % - Methionine 0.58 % - Phenylalanine 1.48 % - Proline 2.4 % - Serine 1.41 % - Threonine 1.07 % - Tryptophan 0.32 % - Tyrosine 0.88 % - Valine 1.38 % - Arabino-xylan Oligosaccharide 7.5 % - Xylo-Oligosaccharide 10.7 % - Mannan-Oligosaccharide 3.0 % - Fructo-Oligosaccharide 0.5 % - Beta-glucan 2.5 % - Dietary Fiber 39.0 % - Soluble Fiber 9.0 % - Insoluble Fiber 30.0 % - Prebiotic Oligosaccharide Content 24.2 % -
Technical Details & Test Data
- Describing the Ileal Microbiota Development in Broilers When Fed Varying Levels of a Yeast Fermentate Product
Introduction
As the poultry industry continues to remove anitbiotic growth promoters from ever being introduced during rearing, alternatives continue to be explored that can improve performance and promote the health of the bird, including through gastrointestinal modulation. Previously, yeast-derived fermentation products have previously been shown to potentially modulate the gastrointestinal microbiota composition, which has implications on bird health and development.
Objective
The objective of the current research was to determine the effects on the ileal microbiota development in broilers fed increasing levels of a yeast-derived fermentation product, ProBiotein®.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that supplementating ProBiotein® would beneficially alter the ileal microbial ecology.
Methods
- 400 male Ross 308 chicks were placed into batteries, where 10 birds each were placed into a total of 40 pen between two batteries. On d 14, birds were moved to 8 floor pens, where all chicks receiving the same treatment from each battery (4 pens) were combined into a single floor pen such that the same blocking design was followed. Birds were fed an industrystandard least cost diet supplemented with the following treatments: 0.00% PB + 0.75% sand; 0.20% PB + 0.55% sand; 0.50% PB + 0.25% sand; 0.75% PB.
- On d 14 and 42, 10 birds per treatment were euthanized and their ileal contents were expressed. The genomic DNA were extracted and samples were sequenced on an Ilumina MiSeq platform. Data were analyzed in QIIME2 for the main effects of treatment and day, and the interaction between. Alpha diversity was analyzed through ANOVA with pairwise differences separated through Kruskal-Wallis. Beta diversity was analyzed through ADONIS, with pariwise differences separated through ANOSIM.
Results
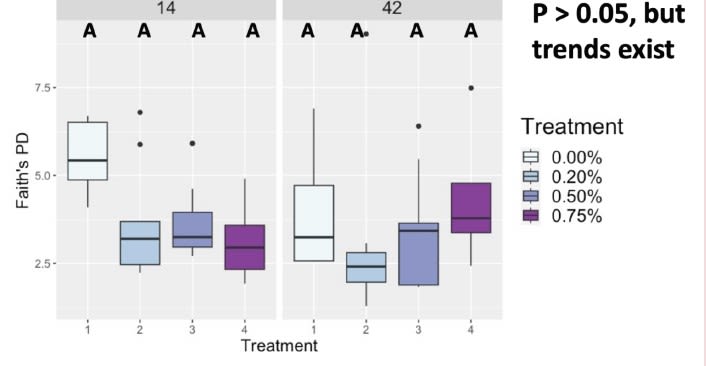
Faith Group Significance
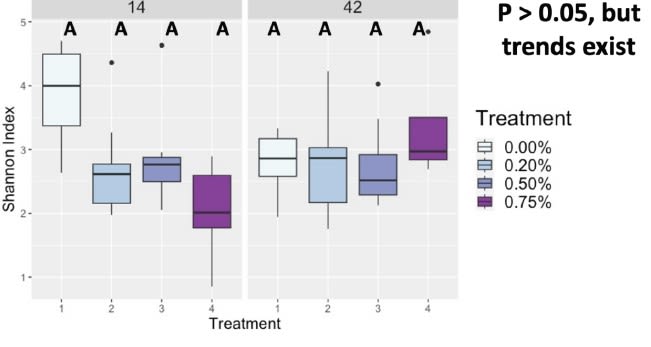
Shannon Group Significance
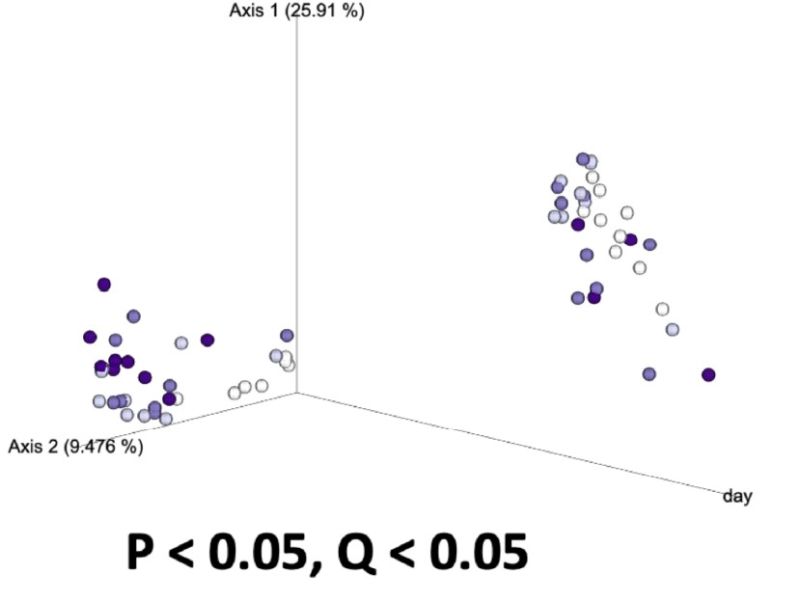
Jaccard
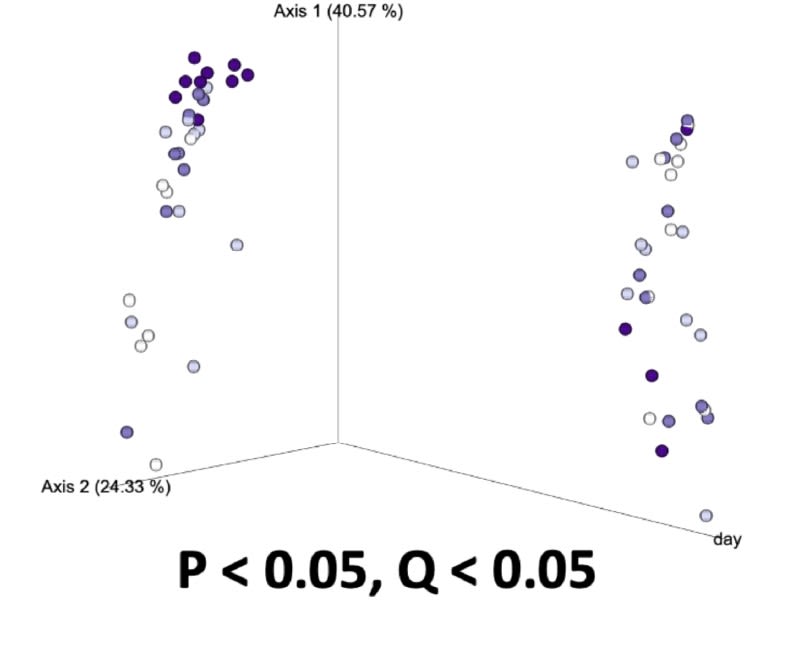
Weighted UniFrac
Eighteen taxa were significantly different in relative abundances, including Lactobacillus, Butyricicoccus, Peptostreptococcus, and Weisella.
Lactobacillus
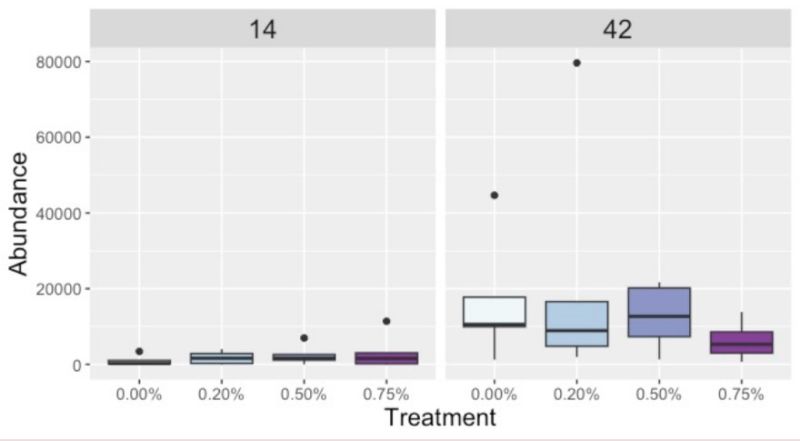
Butyricicoccus
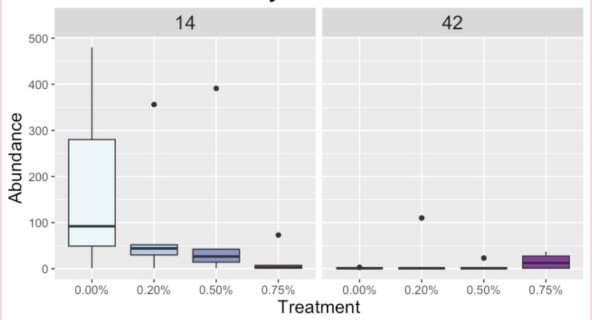
Peptostreptococcus
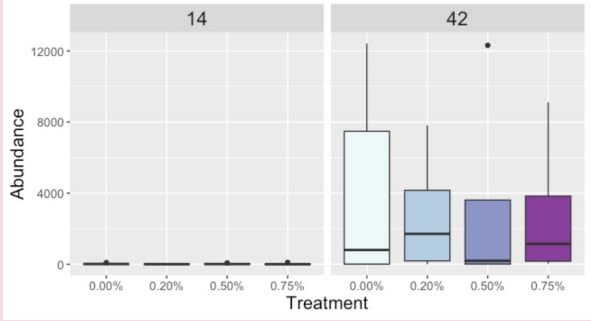
Weissella
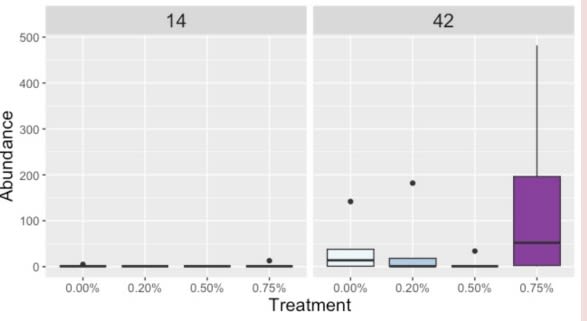
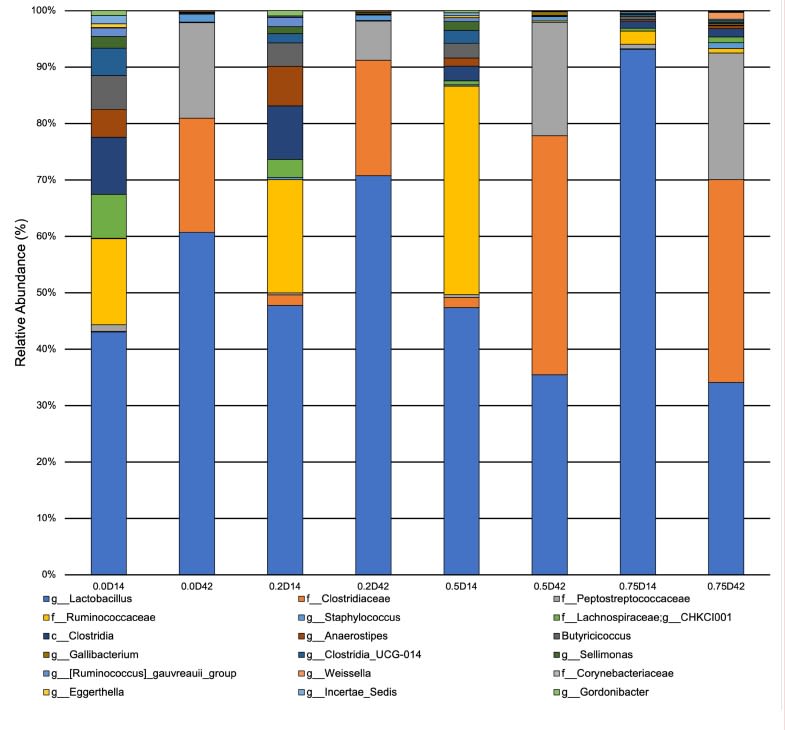
Conclusion
Day was a driving factor in the development of the ileal microbiota composition, but these differences were altered and magnified due to treatment supplementation level. Taxonomical compositions varied due to treatment, with differing relative abundances of previously reported beneficial fermentative taxa, such as Lactobacillus, Peptostreptococcus, Butyriciccocus, and Weisella. Though the overall relationships between ileal microbiota and the host have not been fully elucidated, but have been suggested to promote the immune system's development and alter growth performance, The current results suggest ProBiotein® modulates the microbiota composition and development and may be a beneficial feed amendment for inclusion in poultry diets.
- Impact of a Yeast Fermentate on Salmonella Typhimurium Control in an In Vitro Broiler Intestinal Model
Introduction
- 9 million Americans suffer from foodborne illness per year1
- 40% attributed to land animals
- Salmonella enterica are among the most isolated foodborne pathogens from livestock1,2,3
- Modulation of the broiler gastrointestinal (GIT) microbiota through the use of in-feed supplements has been an effective measure to reduce foodborne pathogens4
Note:
1Painter et al., 2013
2CDC, 2016
3FSIS, 2014, 2016
4Feye et al., 2021Objective
Evaluate the anti-Salmonella effect of varying levels of an in-feed supplement, a yeast fementate (YF), ProBiotein®, in an in vitro GIT model.
Material & Methods
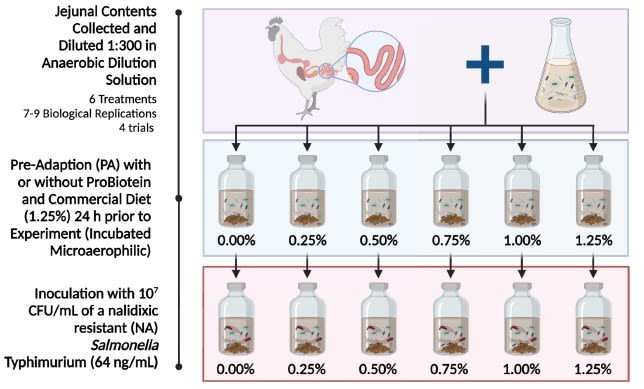
Sampling
Statistical Analyses
- Data were analyzed in JMP® Pro 15
- pH data
- Mixed effect model (random effect=trial)
- Microbiological data
- Mixed effect model (random effect=trial)
- Pairwise differences were determined using Tukey’s HSD with a significance of P ≤ 0.05
Results
Figure 1. Effect of a yeast fermentate on the in vitro intestinal pH (P < 0.05)
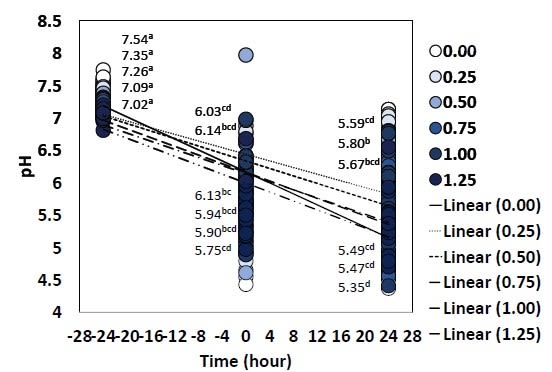
- Time impacted pH more than treatment
- Numerically, 1.25% had lowest pH at 24 h (5.35 pH)
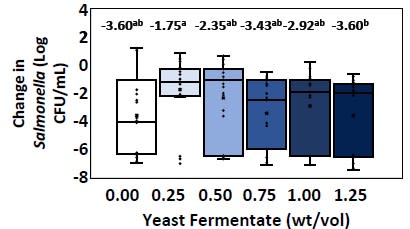
- Treatment 1.25% (-3.604 Log CFU/mL) had greater change in Salmonella than 0.25% (-1.748)
Figure 2. Effect of a yeast fermentate on Salmonella change (P < 0.05)
Conclusion
These results demonstrate the potential of ProBiotein® as an in-feed anti-Salmonella broiler supplement.
- 9 million Americans suffer from foodborne illness per year1
- Mitigation of Salmonella Typhimurium in an In Vitro Broiler Cecal Culture with a Yeast Fermentate
Introduction
- 9 million Americans suffer from foodborne illness per year1
- 40% attributed to land animals
- Salmonella enterica are among the most isolated foodborne pathogens from livestock1,2,3
- Modulation of the broiler gastrointestinal (GIT) microbiota through the use of in-feed supplements has been an effective measure to reduce foodborne pathogens4
Note:
1Painter et al., 2013
2CDC, 2016
3FSIS, 2014, 2016
4Feye et al., 2021Objective
Evaluate the anti-Salmonella effect of varying levels of an in-feed supplement, a yeast fementate (YF), ProBiotein®, in an in vitro GIT model.
Material & Methods

Sampling

Statistical Analyzes
- Data were analyzed in JMP® Pro 15
- pH data
- Mixed effect model (random effect=trial)
- Microbiological data
- Mixed effect model (random effect=trial)
- Pairwise differences were determined using Tukey’s HSD with a significance of P ≤ 0.05
Results
Figure 1. Effect of a yeast fermentate on the in vitro intestinal pH (P < 0.05)

- Time impacted pH more than treatment
- Numerically, 1.25% had lowest pH at 24 h (5.35 pH)
- Treatment 1.25% (-3.604 Log CFU/mL) had greater change in Salmonella than 0.25% (-1.748)
Figure 2. Effect of a yeast fermentate on Salmonella change (P < 0.05)

Conclusion
These results demonstrate the potential of ProBiotein® as an in-feed anti-Salmonella broiler supplement.
- 9 million Americans suffer from foodborne illness per year1
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
- Probiotein Inclusion Rates
Poultry 4 lbs/ton | Multi-Species 4 lbs / ton
- Beef (Stocker/Finisher/Breeding): 4 g (0.141 oz) / hd
- Beef (Receiving Calves/Show): 8 g (0.282 oz) / hd
- Dairy (Lactating/Non-Lactating Cows): 8 g (0.282 oz) / hd
- Swine (Lactating Sow): 8 g (0.282 oz) / hd
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 24 months
- Storage Conditions
Store at temperatures < 115º F
Best if used within 24 months from date of manufacture. Storing in a cool, dark location helps to preserve product freshness.