Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Active Component
- Carrier
- INCI Name
- Ingredient Origin
- Cosmetic Ingredients Functions
- EINECS-No.
- 231-791-2, 234-394-2, 201-069-1, 208-534-8, 246-376-1, 285-379-2, 281-672-4, 200-289-5
- Technologies
- Product Families
- Composition
- The Lotus extract is obtained from flowers of Nelumbo nucifera.
- Oligo- and polysaccharides: fructose, fucose, galactose, glucose, rhamnose, saccharose, starch, xylose.
- Phenolic compounds: anthocyanins, flavonoids (catechins, kaempferol, luteolin, quercetin, rutin), phenolic acids (ellagic), polyphenols.
- Amino acids and proteins
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Labeling Claims
- Product Background
Lotus - Hydrosoluble extract
Antioxidant - Soothing – LighteningNelumbo nucifera: The lotus, Nelumbo nucifera, is present in tropical and subtropical areas. It has white, yellow, pink, red or blue flowers. The sacred lotus, also called oriental lotus, is a perennial aquatic plant with rhizomes (often mistakenly called "roots") that grows in mud from the bottom of lakes and lagoons. Its large leaves rise on the surface of the water on petioles of 1 to 2 m long. The water-repellent surface of the leaf is at the origin of the expression "lotus effect". This expression describes the selfcleaning ability of leaves, which limits adhesion. For more than 200 years, botanists have known that the flowers of several plants become warm during flowering. Indeed, the flowers or inflorescences of some plants with primitive seed are able to regulate their temperature during the process of flowering. These flowers modulate the rate of heat production to keep the temperature higher than the surrounding temperature. The sacred lotus flowers, Nelumbo nucifera, are highly thermogenic and thermoregulator. The temperature inside the flower itself is generally constant between 30-36°C during the hatching of the flowers, in spite of the possible environmental thermal changes ranging from 10 to 45°C. This very particular phenomenon is widely studied to know the specific mechanisms of this feat of nature.
Did you Know?
For more than 200 years, botanists have known that the flowers of several plants become warm during flowering. Indeed, the flowers or inflorescences of some plants with primitive seed are able to regulate their temperature during the process of flowering. These flowers modulate the rate of heat production to keep the temperature higher than the surrounding temperature. The sacred lotus flowers, Nelumbo nucifera, are highly thermogenic and thermoregulator. The temperature inside the flower itself is generally constant between 30-36°C during the hatching of the flowers, in spite of the possible environmental thermal changes ranging from 10 to 45°C. This very particular phenomenon is widely studied to know the specific mechanisms of this feat of nature.
- Cosmetic Properties
The Lotus extract is a protective extract, thanks to following activities:
- Antioxidant (Srichayanurak
- Soothing
- Moisturizing
- Astringent & Lightening
Applications & Uses
- Application Format
- Skin Care Applications
- Treatment Product Applications
- Traditional and Medicinal Uses
The lotus has been cultivated in China for more than 3,000 years, not only for its cultural and ornamental value, but also for medicinal purposes and for its edible seeds and rhizomes. In China, Japan and India, for example, the rhizomes are roasted, pickled, confit or sliced and fried like fries, and a dough is used to make traditional Chinese pastries. Young leaves, petioles and flowers are eaten as vegetables in India. Traditional medicine uses the whole plant. The lotus contains a significant amount of starch, vitamins and asparagine. The seeds are used for their toning properties. The rhizomes and the leaves are more particularly used for their astringent virtues. In Ayurveda and popular medicine, this plant is also used as a diuretic, anthelmintic, and in the treatment of inflammation of the tissues, skin conditions, leprosy, nervous exhaustion, and as an antidote to poison. In India, the plant is traditionally used for its emollient and calming properties in burning sensations. More particularly, the flowers are soothing, astringent, refreshing and useful against rashes and small inflammations. Finally, lotus honey is recommended as a tonic and to treat eye infections.
- Cosmetic Uses
The Lotus extract is a protective extract, thanks to following activities
- Antioxidant
- Soothing
- Moisturizing
- Astringent & Lightening
Therefore, the Lotus extract is recommended for
- Protective care
- Anti-age range
- Complexion products
Properties
- Physical Form
- Appearance
- Liquid
- Odor
- Characteristic
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Plant Rate Implementation Extraction approx. 10 % - Natural Content 74.9 % ISO 16128 Natural Origin Content 99.5 % ISO 16128 Organic Content 43 % ISO 16128 Organic Origin Content 43 % ISO 16128 - Quantifications
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Potassium Sorbate Content 0.13 - 0.17 % GT233 Sodium Benzoate 0.27 - 0.33 % GT233 - Physico-Chemical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Refraction Index 1.350 - 1.380 - GT007 Solubility 10% in Water Soluble - GT004 Specific Gravity 1.020 - 1.100 - GT008 pH Value 3.4 - 4.0 - GT005 - Microbiological Values
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Detection of Enterobacteria Absence - ISO 18415 Enumeration of Mesophilic Aerobic Bacteria max. 100 ufc/mL - cfu/mL ISO 21149 Enumeration of Yeasts And Moulds max. 100 ufc/mL - cfu/mL ISO 16212 - Composition
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Aqua 74.55-75.05 % - Citric Acid max. 1 % - Glycerin min. 23 % - Nelumbo Nucifera Flower Extract 0.5-1 % - Potassium Sorbate 0.15 % - Sodium Benzoate 0.3 % -
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
- Note
- Raw material certified by ECOCERT Greenlife according to Natural & Organic Cosmetics
- Raw material certified by ECOCERT Greenlife according to COSMOS standard
- REACH Status
INCI REACH Status Aqua Water exempted annex IV Glycerin Glycerin exempted: annexe V point 9 Nelumbo Nucifier Flower Extract Exempt: annex V point 8 Citric Acid Citric Acid: registered n°01-2119457026-42 Sodium Benzoate Sodium Benzoate registered n°01-2119460683-35 Potassium Sorbate Potassium Sorbate registered n°01-2119950315-41
Technical Details & Test Data
- Test Data
The Lotus extract forms a protective extract
Antioxidant
Lotus is extremely rich in phenolic compounds such as phenolic acids, anthocyanins or flavonoids, which are very powerful anti-oxidant compounds.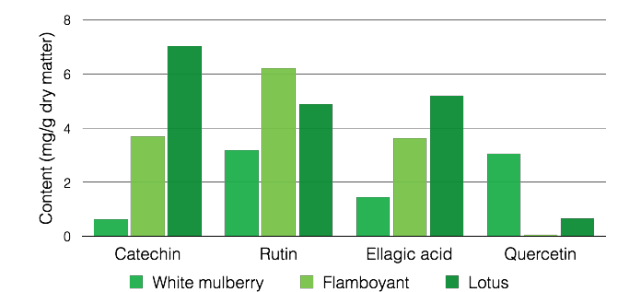
High content in phenolic compounds for lotus
These compounds are able to directly neutralize free radicals, reduce the concentration of peroxide, repair oxidized membranes or reduce the production of reactive species. These molecules inhibit biological oxidation, which induces cell and tissue damage, thus accelerating the mechanisms of skin aging. Thus, the lotus has high antioxidant capabilities, which many studies have shown through various tests and methods.
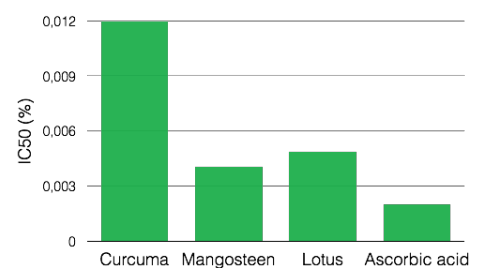
Antioxidant power of lotus: Neutralization of DPPH free radical
- The Lotus extract helps to fight against free radicals and protects cell and membrane structures against damage.
- The Lotus extract is a protective extract: it helps to fight against skin aging
Soothing
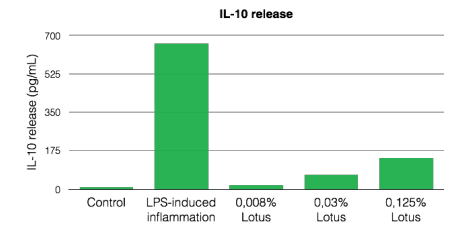
The lotus is traditionally used for its anti-inflammatory properties and to soothe and calm small skin rashes and irritations. Indeed, the flower has calming properties by modulating the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1a, TNF-a and IL-6 and anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10.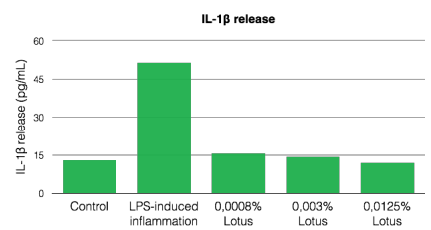
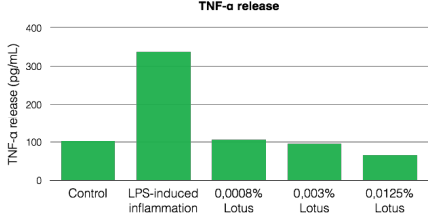
Anti-inflammatory capacity of Lotus: inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine release
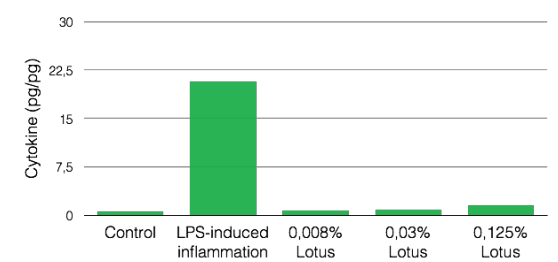
Anti-inflammatory capacity of Lotus: activates anti-inflammatory cytokine release
A specific fraction of lotus flower polysaccharides stimulate cytokine secretion moderately, but especially significantly increases the secretion ratio of anti-/pro inflammatory cytokines (IL-10/IL-6).
Anti-inflammatory power of Lotus
The mechanism of action is mainly due to the fact that the lotus blocks the expression of TLR-2 and TLR-4 (Toll-Like Receptor) mRNA. The signaling pathway of the inflammatory message is then stopped: the intracellular mediators, such as Nuclear Factor-kB, (NF-kB) are no longer activated and secreted; the inflammatory cytokines are much less released.
- The Lotus extract helps to reduce inflammation by regulating the inflammatory response.
- The Lotus extract is a protective extract: it helps to soothe and calm irritated skins
Moisturizing
The lotus has a strong moisturizing activity thanks to its richness in sugars, which participate in two ways of hydration of the skin: the active and passive pathways.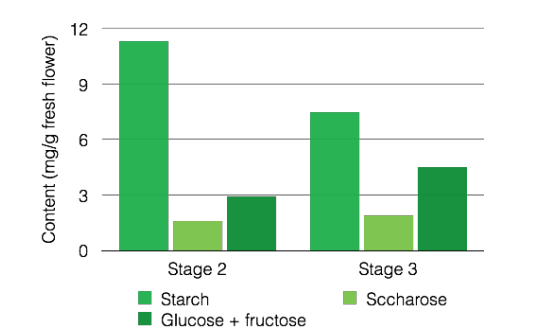
Lotus contains high concentrations of sugars at any stage of ripeness
In fact, the active phenomenon consists of bringing to the skin emollient agents such as humectants (agents that bind water to the surface of the skin) and the components of NMF (Natural Moisturizing Factors), water-soluble substances, hygroscopic and in the stratum corneum. The sugars found in the lotus are hygroscopic molecules, which will capture the surrounding water particles and bind them to the surface of the skin. The Lotus extract thus acts in the active way of cutaneous hydration. On the other hand, the passive phenomenon involves substances that act as a barrier to TEWL (Trans Epidermal Water Loss). The polysaccharides contained in the flower are natural polymers: they will then create a protective film on the stratum corneum, limiting the TEWL. They will reduce water losses by strengthening the impermeability of the epidermis. The Lotus extract thus acts in the passive way of cutaneous hydration. The film thus formed smooths the horny layer; the roughness of Stratum corneum is then reduced and the skin becomes softer to the touch. The lotus therefore helps to reduce small tugging and softens the skin.
- The Lotus extract helps to maintain a good degree of hydration, by connecting the surrounding water molecules. Therefore, it prevents the loss of water and therefore dehydration.
- The Lotus extract is a protective extract: it helps to maintain the water homeostasis of the skin.
Astringent & lightening
In addition, lotus contains many flavonoids. They interact with proteins rich in histamine, glutamine, glycine and especially proline. They bind to these proteins and then form complexes and an accumulation of macromolecules. This phenomenon leads to a precipitation of complexes. Thus, the pores of the skin are tightened. The Lotus extract has astringent properties: the pores are tightened. Phenomena such as acne, bright complexion, oily hair or dandruff are diminished. The lotus has a lightening action on the skin. It helps to homogenize the color of the skin and gives a real shine to the complexion. Indeed, the lotus is able to inhibit the enzymatic activity of tyrosinase, key enzyme of melanogenesis.
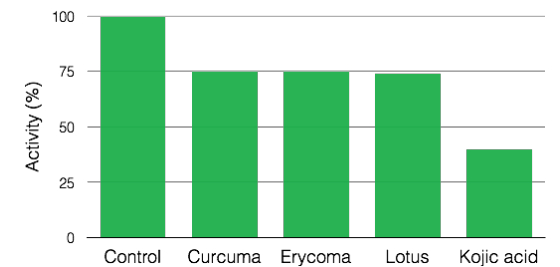
Whitening acticity of lotus: inhibition of tyrosinase activity
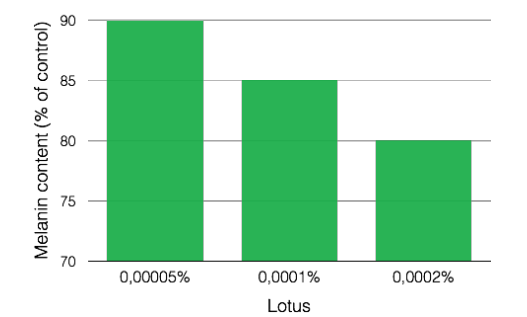 Whitening activity of Lotus: limits melanin content
Whitening activity of Lotus: limits melanin contentAlso, lotus reduces the biological mechanism of melanogenesis from a global point of view, even at very low concentrations.
- The Lotus extract helps to unify the skin color and makes the complexion brighter.
- The Lotus extract is a protective extract: it gives radiance to the complexion.
Storage & Handling
- Shelf Life
- 24 Months
- Storage Conditions
- Keep in the original packaging, without opening, in the recommended storage conditions.
- Stockage
- +15 / +25°C
- Advice before use
- Agitation