Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- INCI Name
- Cosmetic Ingredients Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Labeling Claims
- Product Highlights
A very efficient thickener for a wide array of personal care formulations, designed for unique ease of use, wide compatibility, cost effectiveness and favorable balance of rheological properties.
- Liquid
- Broad pH range stability
- Instant neutralization/thickening
- Highly associative
- Cold-processable
- High surfactant synergy
- Higher efficiency/concentration ratio
- Synergistic rheology with inorganic clays
- Yields clear gels
- Very pseudoplastic
- Foam stabilizer
- High yield value
- Particulate stabilizer
- Thixotropic
- Salt tolerant
- Shear tolerant
- Peroxide compatible
- Formulation compatible
- Polar solvent compatible
- Easy to handle
- Compatible with nonionic, anionic, Zwitterionic and some cationic surfactants
- No preparation necessary
- Non-hygroscopic
- Ability to stabilize suspensions
- Increased manufacturing efficiency
- Mild, soft, non-greasy, non-sticky
- Allows for use of continuous production processes with use of in-line static mixers
- Stable in pH 5.5 to 12 formulations
- Thickens and stabilizes hydrogen peroxide
- Can be processed with membrane pumps and, when diluted, with turbine mixers and high speed propellers
- Does not promote or support contamination, unlike natural thickeners
- Able to formulate clear products
- Supported by comprehensive environmental, health and safety data
- Can be used with electrolytes
- Synergystic interaction with surfactants, particulates and hydrophobic raw materials
- Stabilization of hydrophobic (low solubility) components
- Features of HASE Rheology Modifiers
The chart to the right shows features indicative of the behavior of HASE rheology modifiers under different conditions. Please note that these behaviors may vary to some extent according to specific formulations.
All ACULYN™ rheology modifiers are easy to formulate, have good to excellent salt tolerance, compatibility with anionics and nonionics and low odor. HASE polymers have excellent shear thinning properties and good stability in two-part peroxide systems. Blending of the ASE and HASE chemistries can offer further enhancements and synergies.
Ease of formulation Excellent Associative Yes Salt tolerance NaCl Excellent Di/trivalent ions Good Shear thinning behavior Excellent Solvent compatibility Excellent Low pH compatibility Good Anionic surfactant compatibility Excellent Nonionic surfactant compatibility Excellent Zwitterionic surfactant compatibility Good Cationic surfactant compatibility Some Peroxide stability
One-part system No Two-part system Excellent Lack of odor Excellent
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Application Format
- Bath & Shower Applications
- Color Cosmetic Applications
- Hair Care Applications
- Personal Hygiene Applications
- Skin Care Applications
- Sun Care Applications
- Use Level
- 4 - 8%
- Recommended Applications
- Alcohol and glycol containing formulations
- Body washes and shower gels
- Crystal clear hair care gels
- Crystal clear skin care gels
- Emulsifier free formulations
- Hand and body lotions
- Liquid hand soaps
- Make-up creams and lotions
- Shampoos
- Sunscreen lotions
- Two component hair dye systems (hair dye developers, perm neutralizers)
- Formulation and Use Guidelines
- ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is compatible with surfactants, solvents, oils and salts commonly found in cosmetic and toiletry products. These products undergo instantaneous thickening when neutralized with base.
- This product is supplied as a low viscosity emulsion and can be incorporated directly into formulations with none of the concerns about dissolution, particulate clumping or dusting problems that can be encountered with dry products. ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is also cold processable.
- Because thickening occurs instantaneously upon neutralization with base, in-line mixing with static mixers is possible. Upon neutralization, the ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier emulsion becomes a clear, highly viscous solution.
The preferred order of addition when using ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier in aqueous formulations is as follows:
- Add ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier to the water
- Add other ingredients from the most acidic to the most alkaline
- Add the neutralizing agent
If this sequence is not desirable, ACULYN™ HASE and ASE polymers can be added directly to an alkaline formulation after first diluting the ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier product with two parts of water. Addition of the water prevents gel particles (small particles with neutralized swollen surfaces and unneutralized cores that will take considerable time to dissolve completely).
Preparation of Emulsions and Dispersions
Neutralized ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier thickener can also be used to make oil-inwater emulsions of organic liquids such as mineral oil, lanolin or kerosene. ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier can also be used to suspend fillers and pigments, such as calcium carbonate, silicate clays and titanium dioxide, in water. If ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is being used in an emulsion formulation, the general order of addition is as follows:
- Add ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier to the water phase at temperature
- Add the other water phase ingredients
- Mix separately the oil phase ingredients at temperature
- Mix the oil phase into the water phase maintaining temperature
- Neutralize the ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier polymer
- Cool the mixture with constant stirring
- Add the preservative (if any) at a safe temperature
- Formulation Guidelines
- ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is compatible with surfactants, solvents, oils and salts commonly found in cosmetic and toiletry products. These products undergo instantaneous thickening when neutralized with base.
- This product is supplied as a low viscosity emulsion and can be incorporated directly into formulations with none of the concerns about dissolution, particulate clumping or dusting problems that can be encountered with dry products. ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is also cold processable.
- Because thickening occurs instantaneously upon neutralization with base, in-line mixing with static mixers is possible. Upon neutralization, the ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier emulsion becomes a clear, highly viscous solution.
The preferred order of addition when using ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier in aqueous formulations is as follows:
- Add ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier to the water
- Add other ingredients from the most acidic to the most alkaline
- Add the neutralizing agent
If this sequence is not desirable, ACULYN™ HASE and ASE polymers can be added directly to an alkaline formulation after first diluting the ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier product with two parts of water. Addition of the water prevents gel particles (small particles with neutralized swollen surfaces and unneutralized cores that will take considerable time to dissolve completely).
Preparation of Emulsions and Dispersions
Neutralized ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier thickener can also be used to make oil-inwater emulsions of organic liquids such as mineral oil, lanolin or kerosene. ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier can also be used to suspend fillers and pigments, such as calcium carbonate, silicate clays and titanium dioxide, in water. If ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is being used in an emulsion formulation, the general order of addition is as follows:
- Add ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier to the water phase at temperature
- Add the other water phase ingredients
- Mix separately the oil phase ingredients at temperature
- Mix the oil phase into the water phase maintaining temperature
- Neutralize the ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier polymer
- Cool the mixture with constant stirring
- Add the preservative (if any) at a safe temperature
Properties
- Physical Form
- Appearance
- Milky liquid
- Soluble in
- Water
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Solids Content 20.0 % - pH (as supplied) 3 - - pH (as supplied) 3.5 - 4.2 Acid Number 45 mg KOH/g - Acid Number 45.0 mg KOH/g - Association Very high - - Brookfield Viscosity (LV, Spindle #1, 60 rpm, at 25°C) 0 - 20 cP DOWM 102715 Brookfield Viscosity (of 1% Solids Solution, after 24 hrs at pH 85, RVT Spindle 7, 10 rpm) 35,000-45,000 cP - Density 1.01 - - Equivalent Weight¹ 253 - - Equivalent Weight¹ 253.0 - - Gel Part on 150 Micron 0 - 50 ppm CTG 3240 Gel Part on 45 Micron 0 - 100 ppm CTG 3240 Ionic Nature Anionic - - Rheology Short, non stringy - - Shear Thinning Very high - - Turbidity Solubilized 0 - 25 NTU CTG 3432 Viscosity 20 mPa.s - Viscosity Solubilized (RV, Spindle T-bar C, 10 rpm, 25°C) 25000 - 32000 cP DOWB 508027 Active Content 20 % - Microbiological Values
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Candida albicans Absent per g - Gram Negative Bacteria Absent per g - Staphylococcus aureus Absent per g - Aerobic Plate Count max. 100 CFU/g - - Note
¹ - Grams of dry polymer neutralized by 1 equivalent (40 grams) of NaOH.
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Chemical Inventories
Technical Details & Test Data
- ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier Chemistry
ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is a Hydrophobically-modified Alkali Soluble Emulsion (HASE). HASE polymers are synthesized from an acid/acrylate copolymer backbone and a monomer that connects the hydrophobic groups as side chains. The polymer is made through emulsion polymerization.
ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is synthesized from acrylic acid, acrylate esters and a beheneth-20 methacrylate ester. The general structure for ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is shown to the right.
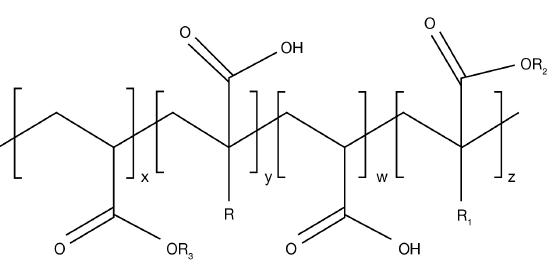
Rx = Acyl chain from 1 to 18 carbons
- Mechanism of Action
- ACULYN™ HASE rheology modifiers are able to thicken by two mechanisms that can act simultaneously and are synergistic, i.e. by the effect of charge-induced polyelectrolytic chain extension and by association of hydrophobe groups.
- When the acid groups present in the ACULYN™ HASE molecules are neutralized with inorganic bases or organic amines, they become anionically charged and water-soluble. ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier thickens above pH 5.5. ACULYN™ HASE rheology modifiers dissolve and swell due to charge-charge repulsion.
- When ACULYN™ HASE polymers swell, the pendant hydrophobic groups are free to build associations with one another and with other hydrophobes available in the formulation, such as surfactants, particulates, emulsion droplets and dyes. This phenomenon creates a network structure that results in a significant viscosity build.
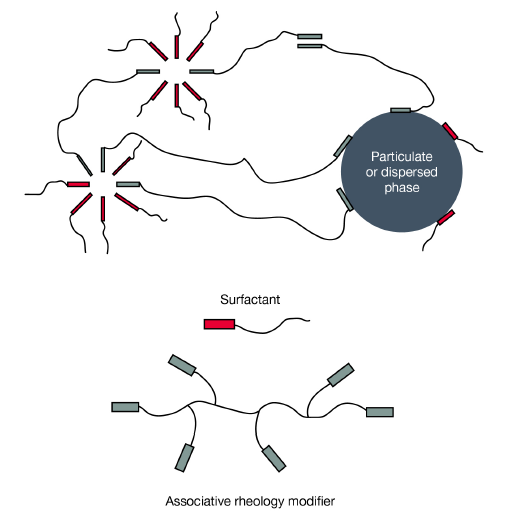
These associative structures can also act to stabilize and disperse particulates in a formulation.
And because of the ethoxylated hydrophobic group on the rheology modifier, ACULYN 28 can also act as a primary emulsifier for some emulsion systems, such as water resistant sunscreens, to minimize the level of surfactant or emulsifier.
- ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier Behavior Profile
ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier possesses many properties that make this polymer highly desirable for use in personal care, as shown by the data presented below.
Rheology
- The highly associative nature of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier has a significant affect on the viscosity of formulations, one that is much stronger than that created by the addition of electrolytes.
- The presence of the C22 hydrophobe causes solutions of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier to be very pseudoplastic with a high yield value, in general showing a high degree of shear thinning. The high yield value also allows the thickener to stabilize suspensions while still being pourable.
- In applications such as two part hair dye products, the shear profile allows for easy application with penetration of the dye, while reducing the dripping or running of hair dye products when developed and applied to the scalp.
- The shear thinning behavior in the following graph is measured in water and the behavior can change in formulations.
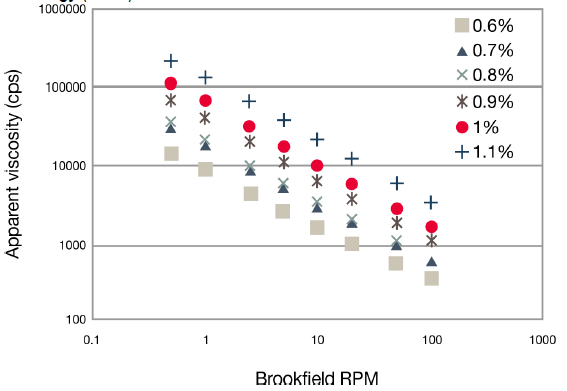
Effect of Shear on ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier at Various Concentrations
In the above graph, the sheer profile is shown for various concentrations of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier (as solid polymer) using a Brookfield Rheometer.
Compatibility
Salt Tolerance
ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier exhibits outstanding salt tolerance. The polymer can significantly build viscosity even in the presence of 1.6% sodium chloride. This performance attribute makes ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier the ingredient of choice in formulations that contain high levels of electrolytes, such as shampoos and shower gels, when the sodium salts of surfactants are employed, or when some raw materials have salt as a trace component.
Effect of Salt Concentration on Gel Viscosity of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier
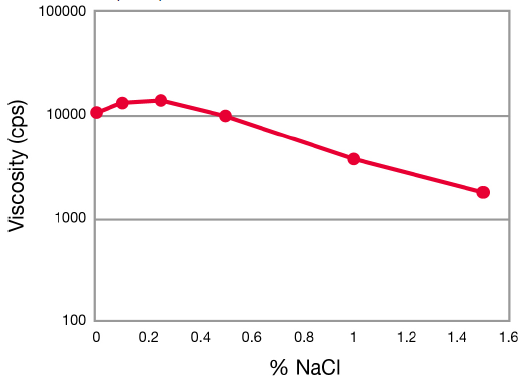
- Polymer concentration: 0.7% solids
- Neutralized with ammonium hydroxside to pH 8.5
- Brookfield LVT, 12 rpm, LV spindle set
pH Tolerance
The thickening effect of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier develops above pH 5.5, when the polymer becomes solubilized and polymer chain extension occurs. In the following graph, where ammonium hydroxide was used as the neutralizing base, the viscosity reaches a maximum and remains steady over a pH range from 6 to 12. This profile will be similar for any neutralizing base.
Profile for Viscosity Versus pH for ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier
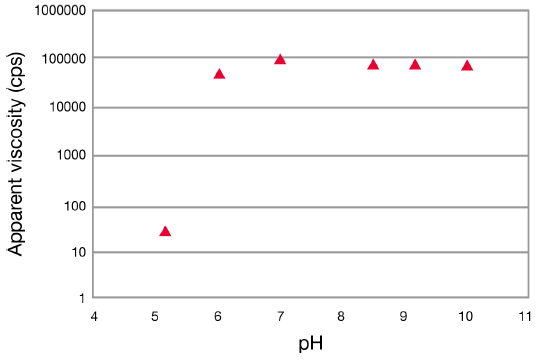
19% polymer solids aqueous solutions neutralized with hydroxide, Brookfield RVT DV I, 10 rpm, Heliopath spindle set.
Surfactant Synergies
- Given that ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is an associative thickener, its thickening efficiency can be significantly affected by the presence of surfactants. The type of surfactant and its concentration play a key role in the rheological properties of the polymer-surfactant system. The measurements of viscosity vs. surfactant concentration generally show an increase in viscosity for ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier-surfactant systems.
- A nonionic surfactant with a high HLB (Hydrophobic Lipophilic Balance), such as C9-11 pareth-12, typically produces a significant increase in viscosity at low concentrations of surfactant that decreases at higher surfactant concentrations. A nonionic surfactant with a low HLB, such as C14-15 pareth-74, leads to a gradual increase in viscosity, which will remain at a higher level even at higher surfactant concentrations.
- In the case of an anionic surfactant such as Sodium Laureth Sulfate (SLES), there is usually a small increase in viscosity at very low surfactant concentrations followed by a gradual decrease at higher surfactant concentrations. The longer alkyl chain in ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier reduces the decrease as compared to many other rheology modifiers.
Clarity in the Presence of Surfactants
Solutions of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier and various surfactants maintain their clarity. The table on the next page shows the clarity of solutions as can be seen from the NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Units) readings above for each of the polymer / surfactant solutions. A solution with a reading below 10 NTUs would be clear. The pH of these solutions was adjusted to 8.5 with ammonium hydroxide, and each system was equilibrated to 20 to 25°C.
Clarity of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier (1% Active) with Different Surfactants
Surfactant % active Brookfield Viscosity (cP, 6 rpm) NTU1 None 0 128,667 < 1.0 Sodium lauryl sulfate
5 2,040 5.3 10 630 5.3 Sodium laureth-3 sulfate
5 17,456 3.1 10 4,044 7.2 Sodium α−olefin sulfonate
5 10,438 2.7 10 2,424 9.6 Cocamidopropyl betaine
5 4,979 5.7 10 885 2.8 C14-15 pareth-7
10 2,067 5.3 20 1,833 4.6 1. NTU = Nephelometric Turbidity Units, a measure of clarity. Lower numbers correspond to a higher degree of clarity.
A reading of 0 to 10 is clear, 10-20 is almost clear, 20-50 has a slight haze.Performance
Extremely Efficient Thickener
The viscosity of neutralized aqueous solutions of ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier as a function of the concentration of solids is shown in the graph opposite. The viscosity of solutions increases with increasing concentration, but even at low concentrations, the viscosity is increased significantly with ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier.
Viscosity of Neutralized ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier with Increasing Concentration
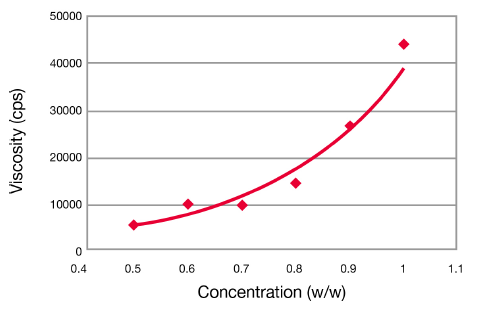
Polymer aqueous solutions neutralized with hydroxide to pH 8.5, Brookfield RVT DV II, 10 rpm, Heliopath spindle set
Clarity of Solutions
The formulation of crystal clear gel products for hair and skin is an important global trend. Based on the low NTU values of the instrumental transparency measurements of aqueous ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier gels, we recommend the use of this product for the preparation of crystal clear formulations.
Solution Clarity of ACULYN™ 22 Rheology Modifier, ACULYN™ 23 Rheology Modifier and ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier Gels
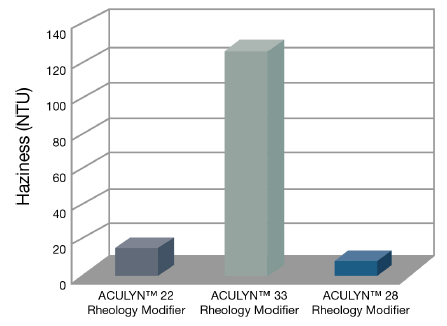
0.7% polymer solides aqueous solutions, Neutralized with ammonium hydroxide to pH 8.5.
Thickening of Alcohols and Polar Solvents
ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier can be used to thicken polar solvents such as ethanol, isopropanol or propylene glycol.
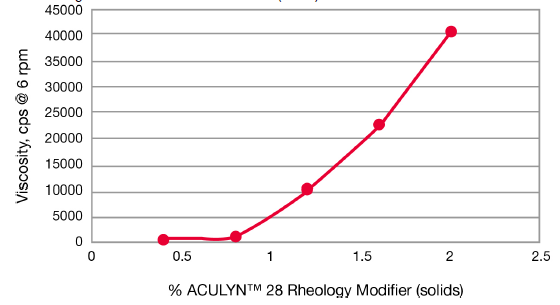
Thickening of 25% Ethanol with ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier
Safety & Health
- Safety Information
Environmental, Health and Safety Record
ACULYN™ 28 Rheology Modifier is considered non-toxic by single oral and dermal exposure, produces minimal to no irritation to the eyes and skin, a non-sensitizer, nonmutagenic in the Ames assay and non-toxic to aquatic organisms, as well as non-irritating or sensitizing in Human Patch testing. This material is safe and appropriate for use in a broad range of rinse-off and leave-on personal care applications.
Disposal Considerations
Dispose in accordance with all local, state (provincial) and federal regulations. Empty containers may contain hazardous residues. This material and its container must be disposed in a safe and legal manner.
Storage & Handling
- Usable Life and Storage
Keep from freezing; material may coagulate. The minimum recommended storage temperature for these materials is 1°C/34°F. The maximum recommended storage temperature is 49°C/120°F. These materials may coagulate if exposed to temperature outside this range. The coagulation process is irreversible.