Enhanced TDS
Knowde-enriched technical product data sheet
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- Technologies
- Product Families
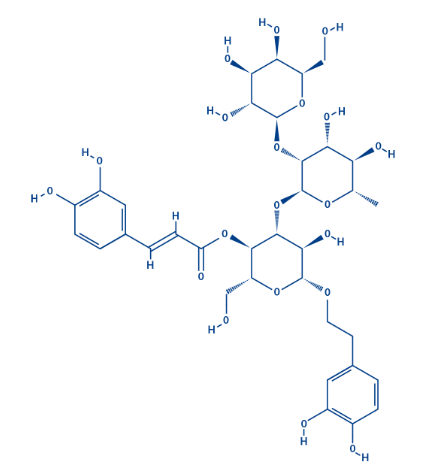
- Chemical Structure
Features & Benefits
- Labeling Claims
- Teupolioside: Ajuga reptans
Ajuga reptans belongs to the Lamiaceae family that consists of 301 native species of Europe, Asia, Africa and naturalized in Oceania and North America (fig.1). Ancient populations used Ajuga for its considerable medicinal effects. Ethnopharmacological surveys revealed that the whole plant was used in folk medicine but the most of its beneficial characteristics reside mainly in leaves and flowers to counteract fever, hemorrage, biliary disorders, high pulse, ulcers and skin diseases.
Ajuga reptans species is nowadays particularly well known for its antibacterial, antimycotic, astringent, diuretic and antineoplastic properties. The most important active ingredient extracted from Ajuga reptans is the phenylpropanoid TEUPOLIOSIDE.
Teupolioside (known also as Lamiuside “A”) is a secondary metabolite produced by the plant for defensive purposes against environmental agents such as UV radiation. Its scarce quantity in the whole plant is the reason why this ingredient can be hardly secured with classical extraction methods.
ABR developed a biotech platform for the production of Teupolioside from suspension cell culture of Ajuga reptans. Due to the Teupolioside structural complexity, also its chemical synthesis is difficult to achieve and the molecule is rarely procurable on the market for its high production cost and very low yield (fig.2).

Applications & Uses
Technical Details & Test Data
- Teupolioside - biological effects
Teupolioside has shown a wide range of activities and it generally acts as an intinflammatory molecule. Moreover, Teupolioside is able to modulate testosterone-related disorders, like juvenile acne, and for the prevention of hair loss in androgenic alopecia.
Specific in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that Teupolioside has beneficial effects also on other pathologic conditions such as:
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
- Crohn’s syndrome and other gastro-intestinal diseases
- Microvasculature diseases